The Death of Sweet Water: Rivers in Bangladesh Face Alarming Decline

Bangladesh, a nation with over 700 rivers, faces an intensifying freshwater crisis. Despite its abundant water bodies, the country faces acute shortages of sweet (fresh) water, particularly during the dry season. This scarcity threatens agriculture, public health, and overall water security.
Causes of Freshwater Scarcity
Upstream Water Diversions
Much of Bangladesh’s freshwater originates from transboundary rivers, notably the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna, which flow from neighboring countries. Structures like the Farakka Barrage in India have altered natural flow patterns, reducing freshwater availability downstream in Bangladesh. This diminished flow exacerbates salinity intrusion in coastal regions, adversely affecting agriculture and potable water sources.
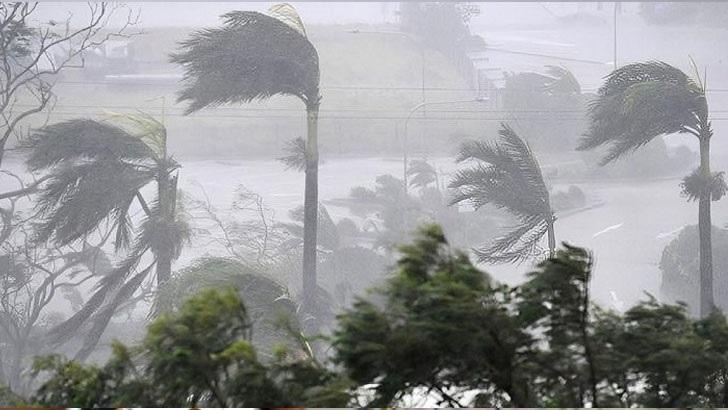

Climate Change and Sea-Level Rise
Bangladesh is highly vulnerable to climate change impacts, including rising sea levels and increased frequency of cyclones. These phenomena lead to saltwater encroachment into freshwater systems, particularly in coastal areas like Khulna and Satkhira. The intrusion compromises drinking water quality and agricultural productivity.
Pollution of River Systems
Industrial discharge, untreated sewage, and agricultural runoff have severely polluted significant rivers such as the Buriganga, Shitalakkha, Turag, and Balu. The contamination renders the water unsafe for consumption and diminishes its usability for irrigation and other purposes.
Groundwater Depletion and Contamination
Over-extraction of groundwater, especially in urban centers like Dhaka, has significantly dropped water tables. Moreover, arsenic contamination and salinity in groundwater sources further limit access to safe drinking water in various regions.
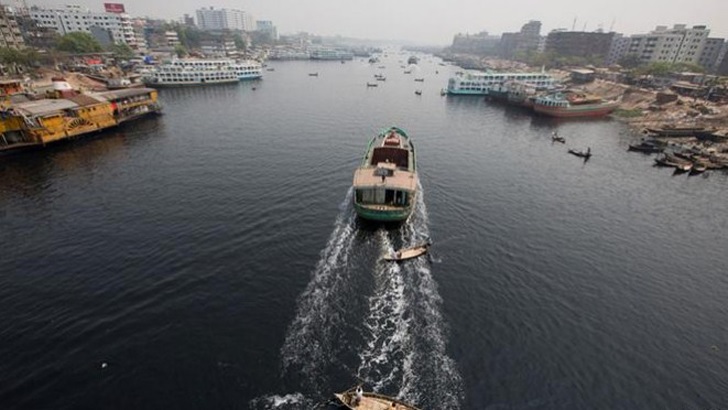
Consequences
- Public Health Risks: Consumption of saline or contaminated water has been linked to health issues such as hypertension, kidney diseases, and complications during pregnancy.
- Agricultural Challenges: Salinity intrusion and water scarcity hinder crop production, threatening food security and farmers’ livelihoods.
- Economic Impact: The freshwater crisis affects fisheries, agriculture, and industry, leading to economic losses and increased poverty in affected regions.
Rivers in Critical Condition
Several rivers in Bangladesh are experiencing severe degradation due to pollution, reduced flow, and mismanagement:
- Buriganga River: Once a vital waterway for Dhaka, it is now heavily polluted with industrial waste and sewage.
- Shitalakkha River: Subject to significant industrial pollution, affecting water quality and aquatic life.
- Turag River: Encroachment and waste dumping have severely narrowed and polluted the river.
- Balu River: Faces contamination from industrial effluents and encroachment issues.
- Karnaphuli River: In Chittagong, this river suffers from industrial pollution and sedimentation.

A study by the University of Glasgow found that none of Bangladesh’s rivers remain within the safe operating space (SOS), indicating widespread ecological stress.
Mitigation Strategies
- Transboundary Water Management: Strengthening agreements with upstream countries to ensure equitable water sharing during dry seasons.
- Pollution Control Measures: Implement stricter regulations on industrial effluents and promote wastewater treatment to reduce river pollution.
- Rainwater Harvesting and Aquifer Recharge: Encouraging rainwater collection and artificial recharge of aquifers to replenish groundwater levels.
- Desalination and Water Purification: Investing in technologies to desalinate brackish water and purify contaminated sources for safe use.
The freshwater crisis in Bangladesh is a multifaceted issue stemming from both anthropogenic activities and climatic factors. Addressing this challenge requires integrated water resource management, regional cooperation, and investment in sustainable water infrastructure to ensure the availability of safe and sufficient freshwater for all.