“UK’s Most Complete Dinosaur Fossil in a Century Reveals New Species, Comptonatus chasei”

125-Million-Year-Old Fossil Unveiled
A newly discovered plant-eating dinosaur species, Comptonatus chasei, roamed an island off England’s southern coast 125 million years ago, recent research reveals.
Size and Significance
This dinosaur, comparable in size to a large American bison and weighing around a ton, was a herding animal, according to Jeremy Lockwood, a doctoral researcher at the University of Portsmouth and lead author of the study. The fossil, unearthed on the Isle of Wight in 2013, is the most complete dinosaur skeleton found in the UK in over a century.
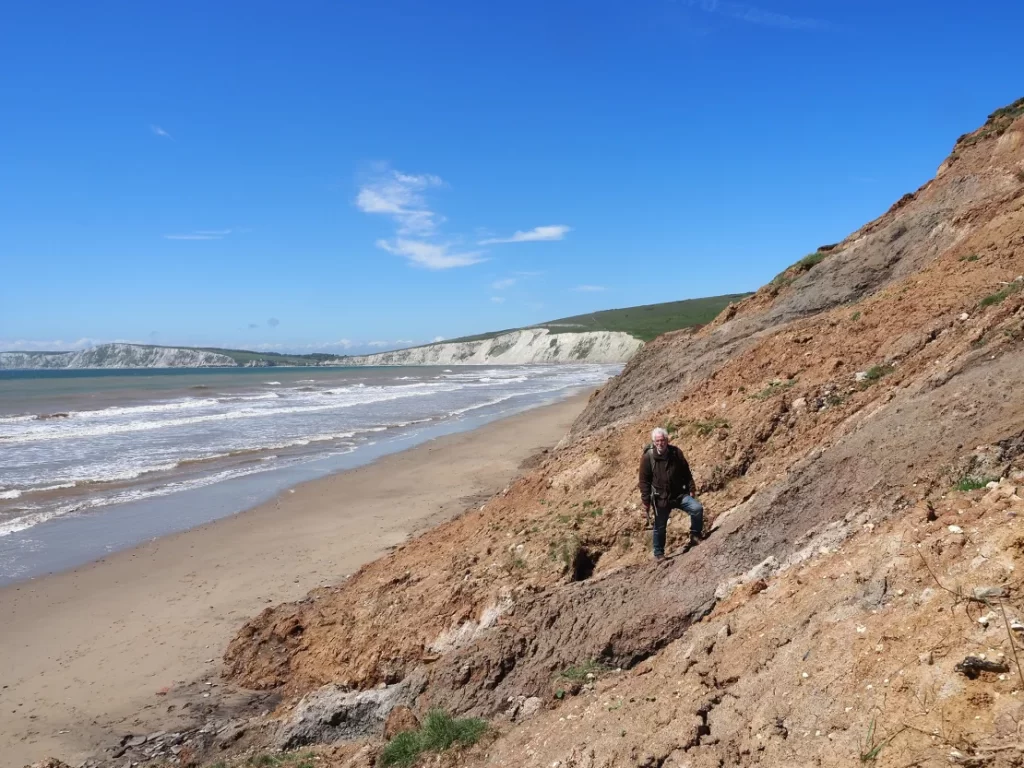

Discovery and Dedication
Avid fossil collector Nick Chase, who passed away in 2019, discovered the 149-bone skeleton. Lockwood likened Chase to the renowned 19th-century paleontologist Mary Anning, praising his dedication to fossil hunting.
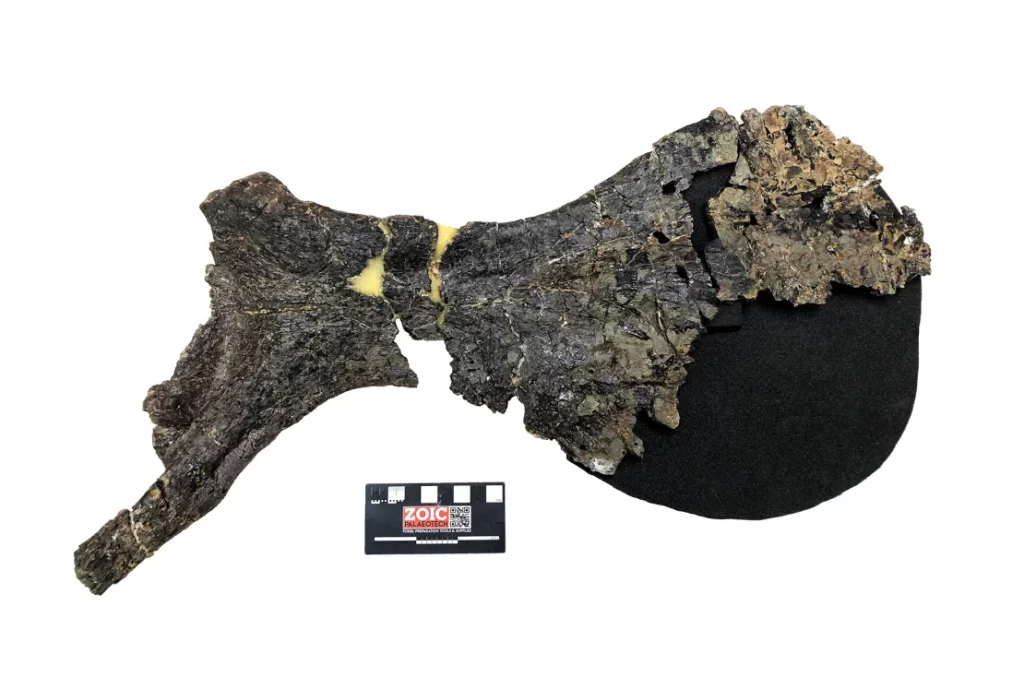

Scientific Impact
Named after Chase and Compton Bay, where it was found, Comptonatus chasei was identified as a new species due to distinct features such as its jaw and unusually large pubic bone. Lockwood emphasized the discovery’s significance in understanding Early Cretaceous dinosaurs in England.
Paleontological Importance
Mike Greenslade of the National Trust highlighted the fossil’s discovery as a testament to the Isle of Wight’s rich paleontological history and the importance of preserving such landscapes.